meist superior
Abnormale Mündung der RUPV in RA
TTE häufig schwierig
Lancellotti P and Cosyns B (2016). Lancellotti, P; Cosyns, B The EACVI echo handbook. Oxford University Press. Oxford.
meist superior
Abnormale Mündung der RUPV in RA
TTE häufig schwierig
Lancellotti P and Cosyns B (2016). Lancellotti, P; Cosyns, B The EACVI echo handbook. Oxford University Press. Oxford.
unroofed Coronarsinus mit Verbindung zum LA
im A4C-Blick oder PLAX: fehlende Grenze zwischen CS und LA
Lancellotti P and Cosyns B (2016). Lancellotti, P; Cosyns, B The EACVI echo handbook. Oxford University Press. Oxford.
Meist klappennaher Defekt
Meist mit MV-Defekten (Cleft) assoziiert, deshalb häufig MR
Lancellotti P and Cosyns B (2016). Lancellotti, P; Cosyns, B The EACVI echo handbook. Oxford University Press. Oxford.
Ostium secundum-Defekt
zentral gelegen
teilweise multiple (=fenestriertes Septum)
Anlotungen: subcostal, A4C, PSAX
RIM-Messungen in Richtung MV, AV, IVC, RUPV
TOE für transcatheter ASD-Verschluss in 90 Grad (bicaval)
cave: der Ostium secundum Defekt ist ein Defekt des Septum primums:
An ostium secundum ASD most often occurs as the result of a true deficiency of septum primum tissue; it is the most common form of a true ASD. The superior and posterior margins of the defect are composed of the septum secundum, the anterior margin is composed of the AV canal septum, and the inferior margin is composed of the septum primum and left venous valve of the inferior vena cava.18 These defects can vary in shape and can be elliptical or round (Figure 8). With large ostium secundum defects, the septum primum is often nearly or completely absent (2)
TEE: Bicavaler Blick: oberer Sinus Venosus Defekt mit einem nicht restriktiven L-R-Stunt in Höhe der Vena cava superior. RA dilatiert. © BUR
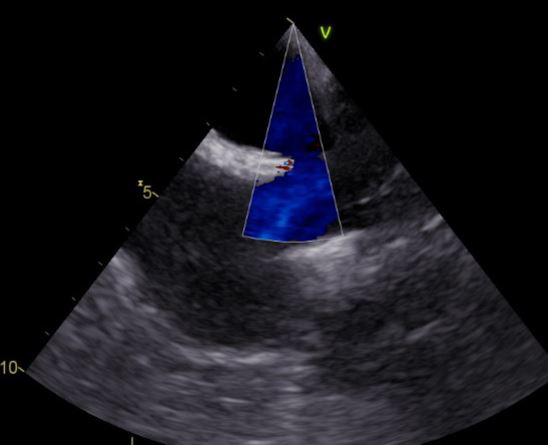
Kann häufig transthorakal nicht gesehen werden
Hyperdynamischer RV
RV-Dilatation,
RVOT-VTI erhöht (Volumenbelastung RV)
Farbdoppler
Kontrast: Auswascheffekt
Re PVe münden in Vena cava superior
